What Is Damping Ratio Formula
They say that the shock valving is 180 75 what means 1800n for rebound and 750n for compression at 0 52m s maybe i misunderstood milliken but it looks like f c dx dt and dx dt is the velocity 0 52 ccrit 2 sqrt km damping ratio is c ccrit.
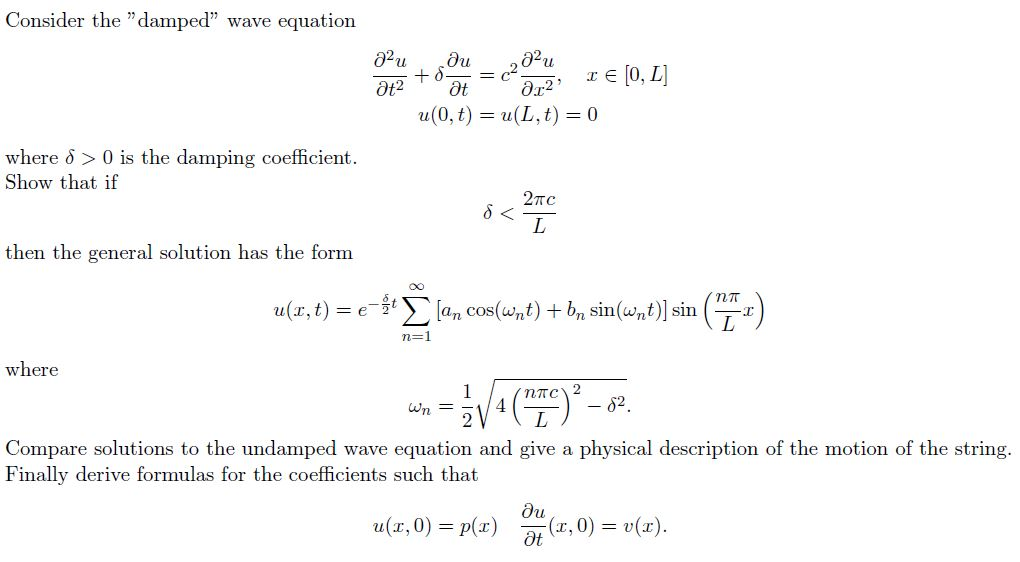
What is damping ratio formula. The damping ratio is a system parameter denoted by ζ zeta that can vary from undamped ζ 0 underdamped ζ 1 through critically damped ζ 1 to overdamped ζ 1. D f z l o a d z s o u r c e. Z s o u r c e. Displaystyle z mathrm source output impedance are shown in the diagram.
Trooper in engineering the damping ratio is a dimensionless measure describing how oscillations in a system decay after a disturbance. Since the actual damping coefficient is 1 ns m the damping ratio 1 63 2 which is much less than 1. Critical damping coefficient 2 x the square root of k x m 2 x the square root of 100 x 10 63 2 ns m. Since the actual damping coefficient is 1 ns m the damping ratio 1 63 2 which is much less than 1.
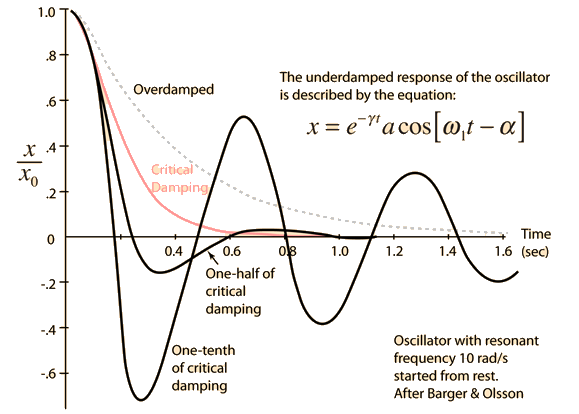
So the system is underdamped and will oscillate back and forth before coming to rest. The behaviour of oscillating systems is often of interest in a diverse range of disciplines that include control engineering chemical engineering mechanical engineering structural engineering and electrical engineering. So the system is underdamped and will oscillate back and forth before coming to rest. Thus with a unit step input.
Displaystyle df frac z mathrm load z mathrm source solving for. These changes indicate that the flexibility of the foundation rock affects the response of the dam in its symmetric vibration modes more than in its anti symmetric modes. Z s o u r c e. Moreover the decreasing proportion of the effective damping due to the flexibility of foundation rock is essentially unaffected by ζsin the range 1.
Formula first contributed by. If we have steady state conditions and the output y is no longer changing with time then d 2y d t2 0 and d y d t 0 and so we have output y kx and k is the steady state gain. What is its damping ratio. A mass suspended from a spring for example might if pulled and released bounce up and down.
I still don t get how to calculate the damping ratio for the data supplied by bilstein.